
Children are more susceptible to injury in their growing age as they are curious to figure out everything on their own. Thus, having basic knowledge of paediatric first aid for the wellness of the child and infant is crucial. When someone is injured, receiving immediate treatment or assistance is crucial. And that is the fundamental concept of paediatric first aid.
Consequently, preserving life and ensuring that the casualty is not in any mortal danger is the aim of paediatric first aid. This article will give you a rundown of various injuries that a child might get into and what sort of paediatric first aid you can provide to them.
Table of Contents
What is Paediatric First Aid?
To provide help to a sick and injured person until full medical treatment is available is what first aid is all about. And paediatric first aid refers to the skills and knowledge you need to provide effective first aid care to children. Read on to learn more about providing effective first aid to children.
Every large institution must appoint a responsible person to be in charge of first-aid arrangements.
Which Institutions Should Have a Paediatric First Aider on Board?
The UK First Aid Regulations strictly emphasises having trained staff on first aid.
You need to have appropriate paediatric first aid training if you are working in any of the following organizations,
- Paediatric nurses
- Sports club staff
- Babysitters
- Play and activity centre job
- Preschool, nursery and school staff
- Childminders
- Parents or families of children and infants
Moreover, it is a crucial requirement for all newly qualified childcarers to have paediatric first aid training. The department of Education guidance makes it compulsory for all nursery and preschool staff.
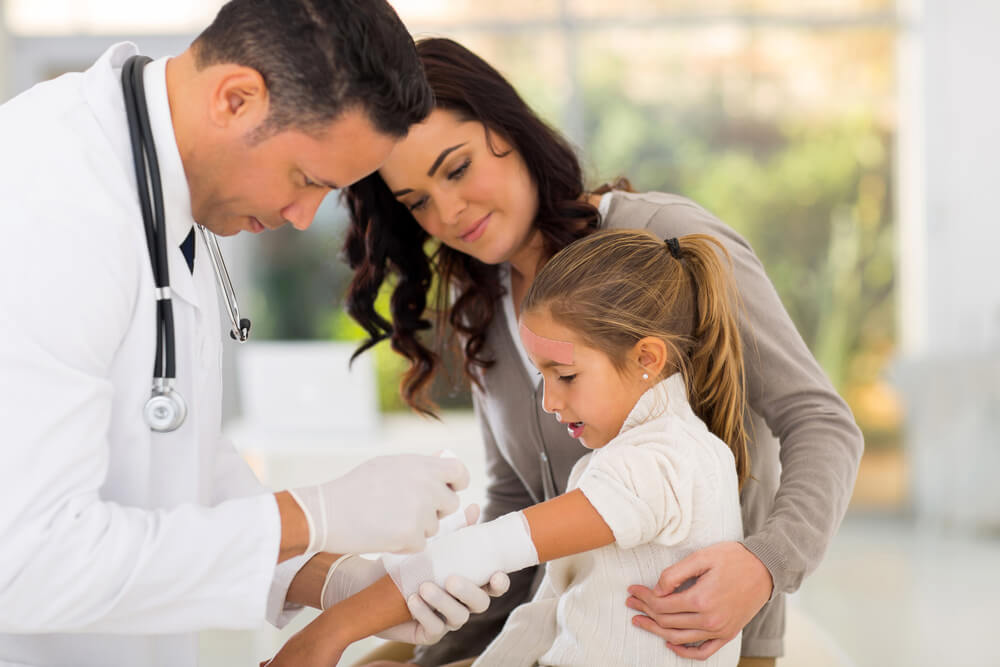

Paediatric First Aid Primary Survey
For the initial assessment and management of a trauma patient, you have to conduct a primary survey. It helps find out and treat life-threatening conditions on a priority basis. Hence, the primary survey is the fast and systematic way to achieve maximum benefits from first aid.
The acronym DRABC assists in performing a primary survey.
- Danger
- Response
- Airway
- Breathing
- Circulation
Danger
The first step in providing first aid is to make sure you are safe and not putting yourself at risk. And you also have to make sure there are no casualties or bystanders before you start your first aid treatment.
Response
Before proceeding further, make sure the toddler or child is conscious or not. You have to gently tap or flick the sole of the foot of the baby. If there is no response, then the child is in an unresponsive state. And you have to get started on paediatric first aid right away.
Airway
The next step in the survey is to identify and treat any life-threatening airway obstruction. Gently place your hand on the forehead of the child if they are unconscious. Next, you have to tilt their head back and slightly prop up their chin with your other hand. And it will ensure the airway is open and clear.
Breathing
If there is any life-threatening problem in breathing, you have to identify and treat it right away. It is the 4th of DRABC principles in paediatric first aid. First, you have to listen and look carefully for any signs in the first 10 seconds. Then, prepare yourself to perform CPR if the child is not breathing normally.
If the condition does not improve, call for emergency assistance on 911. Consequently, ask any bystanders to arrange a defibrillator if possible.
Circulation
If you identify any circulation problem that can be life-threatening, treat it immediately. The primary survey is complete when you finish examining the circulation.
Start CPR right away if the child or toddler is still unresponsive.
Interested in learning more about paediatric first aid? Join our paediatric first aid training course today. The course will teach you all the basics of first aid knowledge in case of an emergency. Furthermore, the accredited course is here to help you learn how to interact with distressed young casualties in pain and keep them calm.
How to Perform CPR on Children?
The full form of CPR is cardiopulmonary resuscitation. When a person’s breathing or heart beating stops, CPR is performed as an emergency lifesaving procedure. CPR is an integral part of providing effective paediatric first aid. It combines chest compressions and rescue breathing.
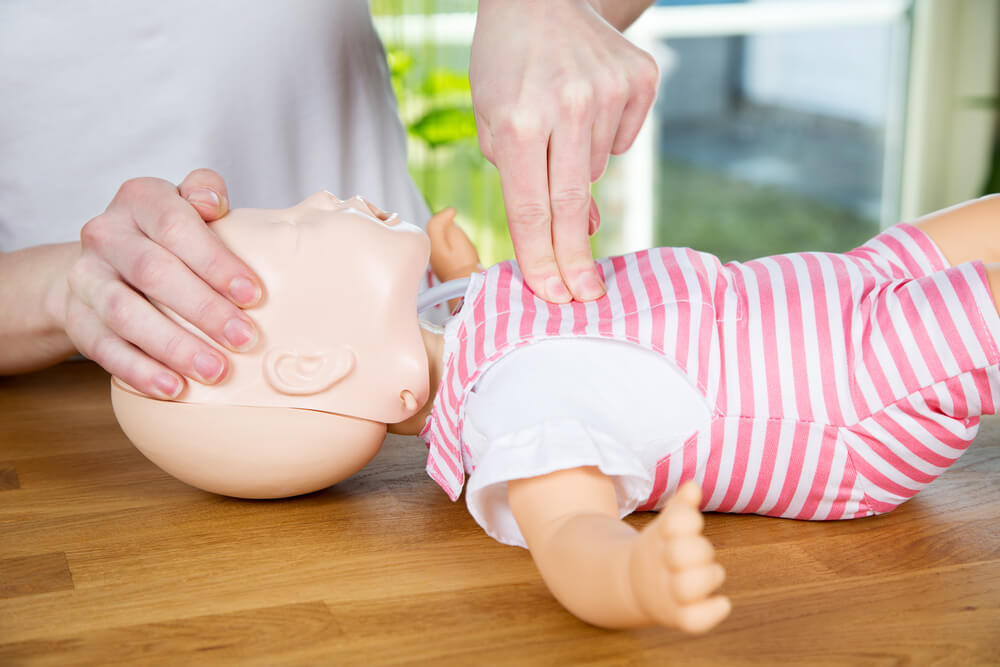

Much emphasis has been put on following the proper techniques of CPR. And you should always perform compression on the lower half of the sternum. Consequently, make sure the toddler or the baby is lying on a flat surface. Because CPR can not be performed in a seated position.
To perform CPR on infants, use the two finger techniques or the two thumbs encircling hands techniques. Moreover, you can use the heel of one hand if the first two techniques are inapplicable. However, using two fingers technique as a single rescuer permits an easier transition from compression to ventilation. And you can easily maintain the head-tilt manoeuvre during compressions. Use your index and middle finger for two finger techniques and place them on the sternum.
Consequently, place a hand or rolled towel beneath the upper thorax and shoulders of the infant or child. It slightly extends the neck and ensures that the targeted compression is reaching the heart. Subsequently, for children, you can perform the compression in the lower half of the sternum using both hands.
For your convenience, we are breaking down the details of performing CPR into the following steps,
Chest Compression Procedure
After pressing down on the child’s chest for two inches or five centimetres, you should pause. You should at least complete 30 chest compressions in this method.
Perform Artificial Breathing
After you have completed 30 chest compressions, tilt the head of the infant and lift their chin to horizontal position. Now provide 5 rescue breaths to re-oxygenate the baby. Make sure to seal your mouth around the baby’s mouth and nose to blow into them. Make sure the chest of the baby is starting to rise. The rise of the chest hints at the airway being opened sufficiently.
Consequently, once the chest is settled, you have to complete another rescue breath. Sometimes, the baby might gurgle vomit when you breathe into them. In that case, briefly turn them onto their side and empty the vomit from their mouth.
Continue Compression & Artificial Breathing
Continuing the CPR until the EMS arrives is a crucial aspect of paediatric first aid. After completion of each set of 30 compressions, make sure to give 2 short and sharp breaths each time. Consequently, keep continuing with the compression soon after performing artificial breathing.
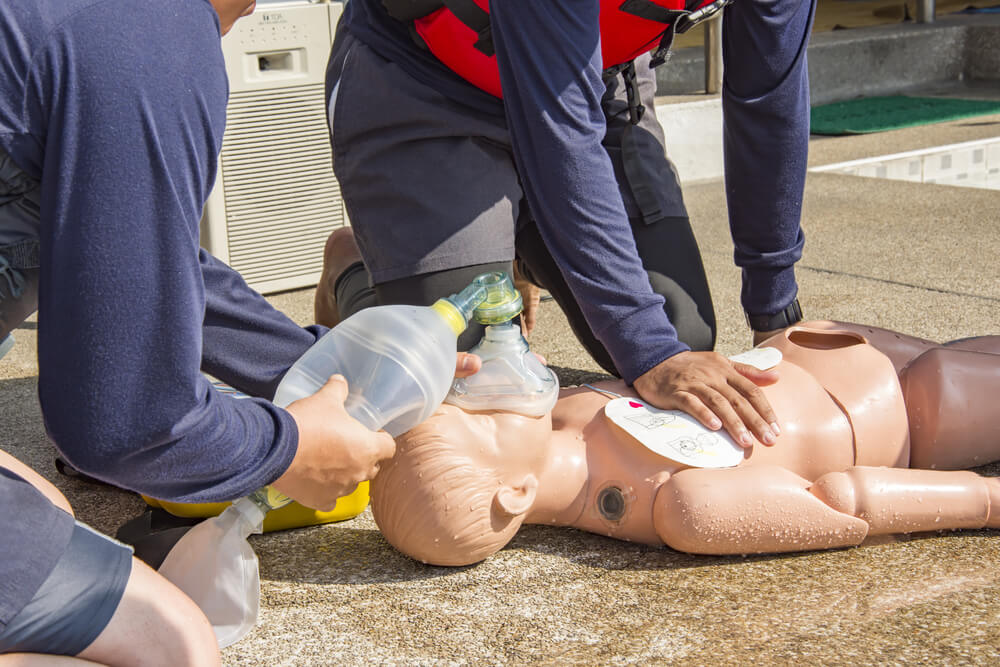
Before you phone for an ambulance, 1 minute of CPR is crucial. It can help in the early recovery of the patient. CPR is a very simple and straightforward procedure. It all comes down to two important steps; modelling the function of the heart and the lungs through compression and artificial breathing.
Importance of CPR in Paediatric First Aid
To survive, every human being needs a constant supply of oxygen. Consequently, brain cells start to die within 3-4 minutes due to oxygen starvation. The procedure of CPR ensures that oxygen is carried into the blood. And consequently, blood carries oxygen into the brain. Thus, performing CPR increases the chances of survival.
In CPR, we have the lifesaving combination of rescue breaths and chest compressions. However, there are some modifications to performing CPR on an infant, as we have discussed. The bones of infants are delicate, so great care should be taken while performing CPR.
Items to Keep in a Paediatric First Aid Kit
Often, we get confused about what items we need to put into the paediatric first aid kit. While there is no legal requirement, there are some basic items every first aid kit should have.

The list of items include,
- Different kinds of bandages
- Sterile gauzes, roller gauzes & eye patch
- Triangular bandages
- Wet Wipes
- Saline solution
- Antibiotic ointment
- Elastic band-aids
- Trauma shears
- Gloves/ Eye protection
- CPR pocket mask
- Clasps and safety pins
- Tourniquets
- Scissors and tweezers
- Syringe & irrigation cap
- Benzoin tincture
- Steri strips
- Adhesive tape and bandages
- Opposite Flexi grip film
- Biodegradable soap
Consequently, the nature of the workplace also determines the content of a first aid box.
Paediatric First Aid for Head Injuries
Toddlers and infants are prone to getting minor head bumps while growing up. It can happen even under strict supervision. However, in case of a severe head injury, a professional doctor should be consulted right away.
You can determine the severity of head injury through the following symptoms.
- The child loses consciousness and feels confused about their surroundings.
- They might have trouble thinking or concentrating. Also, they might show behaviour or personality changes.
- The child appears stunned when faced with a question and answers in a slow manner. Consequently, they might keep repeating the questions.
- The child might have difficulty remembering things and organising themselves.
- They might feel irritable, sad and face difficulties in sleeping.
- Nausea, vomiting, blurry visions, and problems maintaining balance are some other symptoms to keep a lookout for.
Controlling any bleeding and wrapping an icepack in the injured area are primary steps in paediatric first aid for a head injury. If the child remains conscious, keep them under observation for the next 24 hours. It will help you in identifying any worrying signs. Consequently, if the child is unable to walk and cries continuously, call 999 for emergency help.
Paediatric First Aid for Burns & Bleeding
Burns and bleeding are particularly severe for toddlers and infants. Burn damages for toddlers tend to be severe because they have a smaller body surface. So, often a large portion of their skin can get damaged. Consequently, the skin of a baby is 15 times thinner than that of an adult. Thus, the severity of pain and damage is more intense.
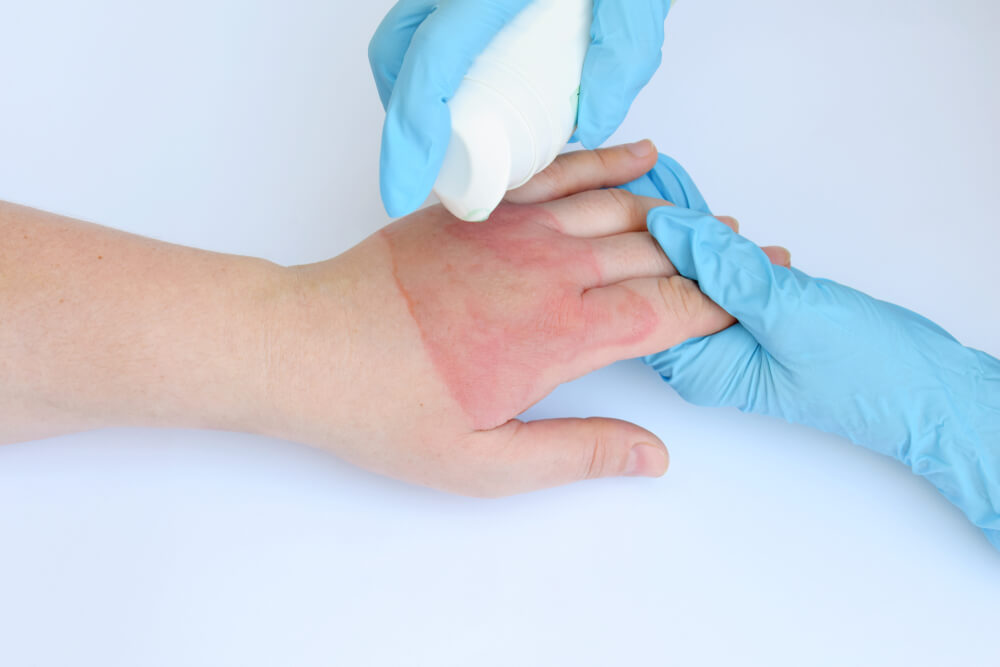
In case of burns, following paediatric first aid is required,
- Do not take clothes off if it is stuck to skin or the skin has blisters.
- Apply water for at least 10 minutes in the affected area. However, keep other parts of the body of the child covered and warm so that they don’t go into shock.
- If a large area is affected, phone an ambulance immediately.
- Do not ever touch the burnt area, and do not apply any lotion or fat onto it.
- Make sure you do not apply tight dressing or tapes without getting the burn assessed by a medical professional.
Consequently, babies only tend to have about a pint of blood in their bodies. And that’s why losing even a small amount of blood can be risky for them. You can take the following primary steps of paediatric first aid in case of bleeding.
- To prevent the baby from fainting or going into shock, lie them down
- To slow down the bleeding, elevate the bleeding area above the heart
- You can apply direct pressure on the wound. And it will stop the blood from coming out.
If the baby starts looking pale and cold, you need to get emergency help right away.
Conclusion
Providing paediatric first aid in the earliest hour of injury increases the probability of a better outcome of medical treatment. It further prevents deterioration of the injured infant’s condition. A quick response to an accident can save lives and minimise the risks.
- Available Courses
- Career Bundles72
- Animal care5
- Law8
- Quality Licence Scheme Endorsed111
- Teaching13
- Teaching & Academics Primary27
- Accounting & Finance Primary30
- Training3
- Design9
- IT & Software44
- Healthcare126
- Marketing31
- Health and Safety402
- Construction48
- Electronics25
- Hospitality22
- Health and Social Care219
- Child Psychology37
- Management375
- Business Skills268
- First Aid70
- Employability264
- Safeguarding75
- Food Hygiene103
- Personal Development1277
 Food Hygiene
Food Hygiene Health & Safety
Health & Safety Safeguarding
Safeguarding First Aid
First Aid Business Skills
Business Skills Personal Development
Personal Development







