
Our electronic gadgets and installation have a lifeline. No matter how high configuration they are, they come with an ultimatum. But this installation may get damaged sooner than expected. This happens if we do not take proper care of our electrical equipment.
Damaged electrical installation is the leading cause of many commercial and industrial losses. This is because damage installation causes a fire hazard. A regular, thorough checkup and a testing scheme help to reduce the electric danger. The checkup also increases our electric appliances and circuit healthline.
The UK’s private landlords need to do a periodic electrical test of their property every five years from June 2020. The time for periodic inspection and testing vary depending on the building’s purpose.
This guide will help you figure out how to ensure the health of the electric wiring and appliances. It gives you a tour of how Periodic Electrical Inspection and Testing happens in the building.
Table of Contents
Periodic Electrical Inspection and Testing

Periodic electrical inspection and testing is the detailed and routine checkup of the electrical systems. It is also known as the Periodic Inspection Report or Periodic Electrical Testing. Certified and professional electrician with relevant and high-quality equipment does the whole process. It minimises electricity-related hazard by detecting faulty wires, corroded parts, missing parts etc.
Periodic inspections and tests aim to:
- To ensure the safety of people, animals and property against electric shock.
- For safety against fire and heat damage to property resulting from wiring defects.
- Confirm that the wiring is not faulty, corroded or damaged, which may cause safety issues.
- Buildings are following wiring regulations enforced by law for safety against electrical hazard.
A periodic electrical inspection and testing will:
- Find any defective electrical work.
- Expose if there is any of your electrical circuits or systems that are getting overloaded.
- Discover any possible dangers of electric shock and fire hazards.
- Check if there is any deficiency of earthing or bonding.
- Installed electronic systems go through tests to check if there are any faulty wires.
Periodic Electrical Inspection and Testing detect electric hazard. It helps get a mortgage or loan against a property. With the report, you can seek compensation from the insurance company upon any damage to the property. It is also required sometimes for a leasing agreement.
Periodic Electrical Inspection and Testing carried out for the whole premises. People can do Portable appliances testing (PAT) for different electronics like heaters, television, etc.
Portable Appliance Testing
Portable appliances testing help to check electrical appliances for safety. In order to avoid harm to staff, health and safety laws ensure that electrical appliances are safe and maintained. It provides continuous protection.
Many equipment manufacturers suggest PIT. The time between tests depends on both the type of system and the setting in which it is to be used. The European Low Voltage Directive regulates the manufacturing of electrical appliances. Compliance with this must be declared and indicated on the product by a CE mark. This is the responsibility of the producer or the importer and is monitored by Trade Standards.
Who is Competent to Carry Out the Testing?
The person who carries out the test must be competent and experienced. They must have a formal qualification of doing the test and know how to use electrical instruments to check installations.
Why are Periodic Electrical Inspection and Testing Needed?

Statistical data have shown that electricity causes around 35 deaths and 4,200 injuries in the UK per year. So the main reason for doing the inspection and testing is to ensure electrical safety. But periodic electrical inspection and testing are also done for many other factors.
- It helps verify the electrical system’s health following the Electricity at Work Act and Health & Safety regulations.
- Electrical wires start to deteriorate after a while for many reasons. The test looks for ageing, corrosion, damage, overheating, excessive use, wear and tear.
- When there is a change in ownership of property or new tenants come.
- People can do periodic inspection and testing when renting a property.
- When selling or buying a property.
- Due to significant changes that electric installation should go under for better update.
- In case of possible damages caused to the electrical system that needs immediate repairment.
- To meet the criteria of the insurance provider. If you do not do the testing, it will impact your coverage and may raise costs.
- The report for periodic testing is necessary for landlords to go through any Housing Association or council.
- Places like banks, insurance agencies, and Councils, Health and Safety departments use the testing report.
Landlords must conduct this test to ensure their house safety for giving it on rent. It can be a criminal offence otherwise. As a penalty, you might have to pay £5000 and six months of imprisonment if there is no proper testing evidence.
How the Periodic Electrical Inspection and Testing Conducted?

Only qualified individuals, such as licensed electricians, may carry out periodic inspection and testing. They shall track electricity conditions following the UK safety standard for electrical installation, BS 7671 – Requirements for Electrical Installations (IET Wiring Regulations).
Regulation 621.5 of BS 7671 requires: “Periodic inspection and testing shall be undertaken by a skilled person or persons, competent in such work”. BS 7671 defines a skilled person (electrically) as a “person who possesses, as appropriate to the nature of work being undertaken, adequate education, training and practical skills, and who is able to perceive risks and avoid hazards which electricity can create”.
Initial verification
All new installations checked if it is compliant with the IET Wiring Regulations BS 7671. The inspection and testing happen during construction and completion of the building. The regulation guarantees the electric system aligns with the designers’ purpose. It also ensures wiring of the building is designed and tested according to BS7671. The initial inspection provides the basis for future Periodic electrical inspections and testing. Through this verification:
- It ensures that all materials and equipment utilised are of the correct type.
- The electrical wiring complies with British Standard European Norm (BS EN) standards. To ensure that all parts of the fixed installation are selected and erected.
- To check if there is any damaged installation that needs fixing.
Periodic inspection and testing
In order to continue to be used safely, periodic inspection and testing aim to provide an engineering view on whether the system is in a good state. This outlines four particular concerns. Three of these apply quite correctly to the ongoing and assured safety of personnel; one directly relates to ‘fire and heat protection against property damage resulting from an installation defect’.
Routine checks vs formal inspections
During the period between these inspections, people can check on the electrical installations often. Wear and tear and other rapture may occur at any time. Such tests don’t necessarily need to be performed by an electrically trained individual, but they need to be completed by someone who can safely use the device and detect defects.
The inspection and testing are done in three steps:
Step 1: Inspection
This is the diagnosis of the electrical health of your building. A qualified electrician will look around the wires, test all your appliances and find all the defects.
The electrician will find wear and tear, breakages or damage of parts and wires. They will look for missing parts like covers and screws, check loose fixings. Then they will look for signs of overheating. Confirm that all the switchgear accessible and the enclosure doors are secure. They also make sure adequate labelling is in place.
Step 2: Operation
In this stage, electricians will try to operate the thing that needs fixing, like the switchgear. They will check equipment by switching on and off. They will also inspect the residual current device (RCD) for the circuits. It is particularly operated in gardens and bathrooms using a test button.
Step 3: Defect Report
The professional electrician will form a report of all the faults and problems in electric installations. The previously identified defects that have been repaired will be included in the report. Reports of any new defects found are prioritised for completion, depending on the seriousness of the finding.
After periodic test completion, you will receive a certificate from your testing engineer. This is also referred to as the Electrical Inspection Condition Report (EICR). Any corrosion, disruption, failures or other unsafe aspects of your electrical system will be outlined in the report, plus anything that is not consistent with current safety requirements or may put people at risk is included in it. The information is given in the form of codes which decreases in seriousness down the number.
- Code 1(C1) Requires urgent attention.
- Code 2(C2) Requires improvement.
- Code 3(C3) Requires further investigation.
- Code 4(C4) Does not comply with BS 7671.
C1 means a hazardous issue that needs immediate attention to make the installation safe. When an electrician has carried out the necessary remedial work, an appropriate certificate will be issued. The certificate confirms that all tests carried out were following BS 7671 regulation.
In the report, the electrician will provide you with a summary of the inspection, which will indicate the electrical equipment condition, taking all the relevant circumstances into account.
Findings are categorised from C1 to C4 by the inspector in terms of their priority. This priority’s primary objective is life protection. So observations such as missing covers or broken switches could be C1 or C2. Before refurbishments or significant changes occur, it is not uncommon for C3 and C4 results to be delayed. However, it is worth looking at the results of C3 and C4. As these could have a more binding effect from a property security point of view and may cause severe damage in the future if not taken into account.
How Often is a periodic inspection required?

How often the periodic inspection will take place depends on the nature of the building and property. It varies for industrial, residential and commercially used facilities. But in a public property where there is a higher use of electricity and electrically installed appliances, the periodic inspections and testing frequency increase because of the possibility of electric hazard. For places with more electric usage, the periodic inspection is every three to four months.
The frequency is also dependent on factors like age, the environment of the installation (such as the water body there should be a regular inspection). The installation designer should consider and recommend the date for the first periodic inspection after installation. A competent person who is conducting the current inspection will determine the frequency of consequent inspections.
This initial inspection will lead to findings and further necessary steps to minimise imperfect installation. For instance, if an installation has not survived its environment’s adverse effects and usage or does not appear to be subject to sufficient or adequate maintenance. The number of inspections increases if there is no previous inspection record available; a 100% inspection of every electrical installation is mandatory.
Below is the summary for the maximum number of years between each inspection for the different premise:
For General Property
- Ten years for an owner-occupied home.
- Five years for a rented home.
- Industrials should be checked every three years.
- Inspect all offices, shops and laboratories should be every five years.
- Educational establishments should be inspected every five years.
- Commercial buildings are also inspected for electrical hazard every five years.
For Publically Open Buildings
- After every three years, owners should carry out the test for leisure complexes, places of public entertainment and theatres.
- Owners must check their restaurants, hotels, public houses, village halls and community centres every five years.
For Special and specific installations
- Swimming pools, Marinas and fish farms owners should do the PIT every year.
- The time gap for laundries and petrol filling stations is also one year.
- Check Construction Site Installations every three months.
- Three years for a caravan.
Electrical Hazards for Inadequate Testing
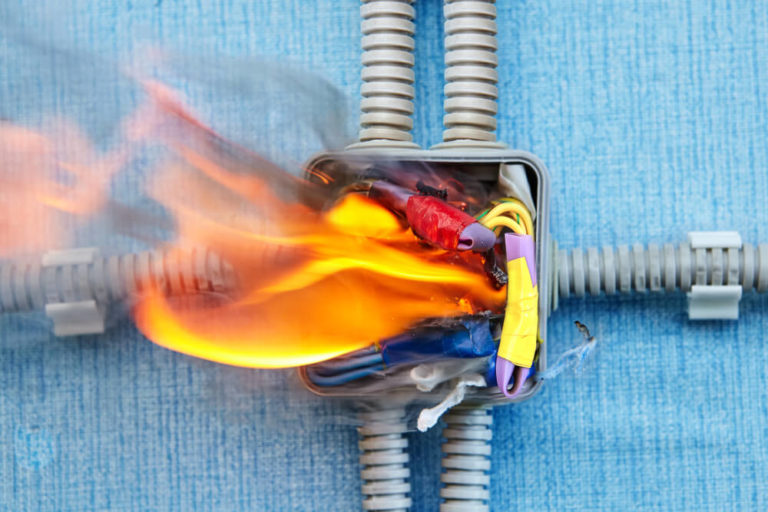
What makes industries and factories function are these gargantuan machinery, which often do not rely on electricity.
The factory machinery operates at high voltages and generates a lot of heat. These conditions render a high probability that the insulation around the copper core wires wears out.
One lethal outcome might be that the circuitry inside a machine is shorted, and if there is current leaking out on their metal surface, workers can be electrocuted.
From time to time, the authority must inspect the wirings.
These high operating voltages emit a lot of heat. Components can overheat and result in an electric fire.
Electrical installation in households also wears out when they get old. They always need proper servicing to function adequately and for safety. If they are not checked in time, a major disaster can take place.
Here are some common electrical hazards that happened due to inadequate testing:
- Inadequate Wiring and Overloaded Circuits- Improperly sized wires cause improper fluctuation of currents. This will cause the circuit to overheat or overload, starting a fire.
- Exposed Electrical Parts– Check lighting, switch box and other electrical appliances regularly for exposed parts or loose insulation parts on electrical cords. Otherwise, this may cause an electric shock to whoever comes in contact with it.
- Improper Grounding– improper grounding or the low maintenance of grounding is a violation of rules. There is a high risk of electrocution due to improper grounding as the extra voltage is not neutralised by proper grounding.
- Damaged Insulation- There is a risk of damaged or inadequate insulation. Be conscious and immediately report damaged insulation. Until removing damaged insulation, switch off all power sources and never cover them with electrical tape.
- Wet Conditions– Water is a great conductor of electricity. Altogether avoid using electric equipment in wet conditions, or there is a significant risk of getting electrocuted.
- Overhead Power Lines– Overhead electricity lines and energy lines have high voltages that can cause employees to experience major burns and electrical exposure.
- Damaged Tools and Equipment– Damaged electrical equipment and tools are hazardous. They may explode or short circuit if not handled correctly or if the damage is not fixed.
Finally, Minimize Electrical Hazard!

Electricity runs the world; we can not imagine even a day without electricity. But at the end of the day, electricity is one of the significant dangers that cost thousands of lives and damages to the property. Many of us are careless while handling our electric appliances and installation while they need the most care. Periodical Electrical Inspection and Testing minimise electrical hazards and improve your electrical installation homes and workplaces’ functionality. So do not forget to do your next Periodical Electrical Inspection and Testing.
Learn More
- Available Courses
- Career Bundles72
- Animal care5
- Law8
- Quality Licence Scheme Endorsed111
- Teaching13
- Teaching & Academics Primary27
- Accounting & Finance Primary29
- Training3
- Design9
- IT & Software43
- Healthcare124
- Marketing31
- Health and Safety400
- Construction48
- Electronics25
- Hospitality22
- Health and Social Care219
- Child Psychology37
- Management370
- Business Skills267
- First Aid70
- Employability264
- Safeguarding75
- Food Hygiene103
- Personal Development1272
 Food Hygiene
Food Hygiene Health & Safety
Health & Safety Safeguarding
Safeguarding First Aid
First Aid Business Skills
Business Skills Personal Development
Personal Development












